When Cancer Patients gets infected with Covid-19: Effects and Risks
Shuvomoy Banerjee, PhD; Neucrad Health desk, Updated on January 14, 2022
Out of the Millions of people losing their lives in the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic worldwide, cancer patients comprise about 6%! Interestingly, the death of cancer patients is not due to only “cancer co-morbidity” but may be some underlying reasons associated with different variants of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Before going to intricate part of this discussion, let’s try to understand first the special relationship between viral infections and cancer.
Cancer and Viruses:
Some specific viruses can cause cancers. A Cancer causing virus is called a “tumor-virus”.
Following are some of the lists of such tumor viruses along with the types of cancer they cause:
- Epstein-Barr virus- May cause B-cell cancers
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated with the herpes virus- May cause skin and B-cell cancers
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)- May cause uterine cancers
- Hepatitis-C virus (HCV)- May cause Liver cancer
- Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus 1 (HTLV-1)- May causes Blood cancers.
Research has shown that tumor-viruses enter inside cells to deregulate important functions of various cellular proteins, transcription factors to increase cell division abnormally. Therefore, uncontrolled cellular proliferation results for on setting cancer. In certain immuno-compromised conditions, such as AIDS, SCID or during organ transplantation when the body’s immune system is found weakened, tumor virus can easily evade the immune barrier and helps in cancer progression. In most cases, the tumor virus can cause metastatic cancer in the body.
Coronavirus Infections and Cancer:
Although coronavirus are not known to cause cancers in humans, they showed their detrimental effects during the MERS pandemic. According to 2015 statistics, during the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Virus (MERS) pandemic, the mortality rate of cancer patients infected with the virus was 74%! Henceforth, for obvious reasons the Scientists and Physicians throughout the globe were seriously concerned about the cancer patients in case of the current Covid-19 pandemic.
Novel Coronavirus Infections and Cancer:
Novel coronavirus just like its cousin virus MERS, cannot cause cancer as the reports are indicating so far. However, the overall death rate of cancer patients for Covid-19 is surprisingly quite low as compared to MERS cases. Researchers and physicians are getting mixed reports from different parts of the world and the reports suggesting higher risks for patients with lung, throat, and nasopharyngeal types of cancers.
Since, SARS-CoV-2 infections can itself lead to serious illness; the treatment of cancer patients due to Covid-19 infections becomes more complicated. In cases where corona patients’ illnesses reach a point of life-threat to the patients, doctors are forced to discontinue the necessary chemotherapy. Henceforth, the Doctors are a bit hesitant about administering chemotherapy to cancer patients with Covid-19 infection. Just like the chemotherapy, other necessary cancer-related tests and surgeries also become immensely disrupted in case of Covid-19 patients sometime leading to indirect cause of deaths.
Why is the risk higher for a cancer patient with Covid-19 infection?
It can be explained in two ways:
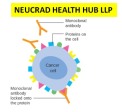
- Scientists have explained that the novel coronavirus enters the cell with the help of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptor. It has been found that in the cases of pancreas, uterus and kidney cancers, the ACE-2 receptors are produced in large quantities therefore making the SARS-CoV-2 infection easy. Surprisingly, ACE-2 receptors are low in breast, liver, and prostate cancers, but there is no clear evidence of the complications of Covid-19.
- Incidentally, the amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines viz. IL-6, IL-17, TGF-beta, TNF-alpha gets elevated in the body of most cancer patients. In this condition, SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause the patient to develop “cytokine storm” symptoms, which can lead to patient’s disability and death.
Treatment of cancer patients with Covid-19:
According to doctors and scientists, anti-cancer therapy and anti-viral therapy can be carried out simultaneously in a cancer patient with Covid-19. However, in this case, some modern medical methods are being used, such as-
- Monoclonal antibody cocktail vaccine: This type of vaccine can quickly target different epitopes of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
- Recombinant ACE-2 receptor conjugated nanoparticle therapy: In general, nanoparticle technology helps to increase the ‘bioavailability’ of a drug. In this case, the ACE-2 receptor is made in a conjugated nanoparticle laboratory that binds to the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and prevents infection in the cancer patient’s body.
- Pro-inflammatory cytokine inhibitor therapy: Inflammation of the cancer patient’s body is reduced by inactivating pro-inflammatory cytokines with specific cytokine inhibitors.
Therefore, treating cancer and Covid-19 together is a real challenge for all the Physicians. In-depth research can be conducted to investigate how SARS-CoV-2 infects normal cells vs. a cancer cell in the body, or whether there is a significant difference in the infection levels between these two cells. Another aspect that needs to be studied is how the same anti-viral drug works in people without cancer and people with cancer. We hope such Basic cancer and Covid-19 research will help to bring out the solution in the near future.
References:
- Gosain R, Abdou Y, Singh A, Rana N, Puzanov I, Ernstoff MS. COVID-19 and Cancer: a Comprehensive Review. Curr Oncol Rep. 2020;22(5):53. Published 2020 May 8. doi:10.1007/s11912-020-00934-7
- ElGohary GM, Hashmi S, Styczynski J, et al. The risk and prognosis of COVID-19 infection in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 30]. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020;S1658-3876(20)30122-9. doi:10.1016/j.hemonc.2020.07.005
- Al-Quteimat OM, Amer AM. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Cancer Patients. Am J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;43(6):452-455. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000712. PMID: 32304435; PMCID: PMC7188063.
- Jyotsana N, King MR. The Impact of COVID-19 on Cancer Risk and Treatment [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jun 29]. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020;13(4):1-7. doi:10.1007/s12195-020-00630-3
- Curigliano G. Cancer Patients and Risk of Mortality for COVID-19. Cancer Cell. 2020;38(2):161-163. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.07.006
- Geisslinger F, Vollmar AM, Bartel K. Cancer Patients Have a Higher Risk Regarding COVID-19 – and Vice Versa?. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(7):143. Published 2020 Jul 6. doi:10.3390/ph13070143
- de Joode K, Dumoulin DW, Engelen V, et al. Impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on cancer treatment: the patients’ perspective. Eur J Cancer. 2020;136:132-139. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2020.06.019
- Liao JB. Viruses and human cancer. Yale J Biol Med. 2006;79(3-4):115-122.
- Schiller JT, Lowy DR. Virus infection and human cancer: an overview. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;193:1-10. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-38965-8_1. PMID: 24008290.