Sexually Transmitted Diseases Through Polygamy
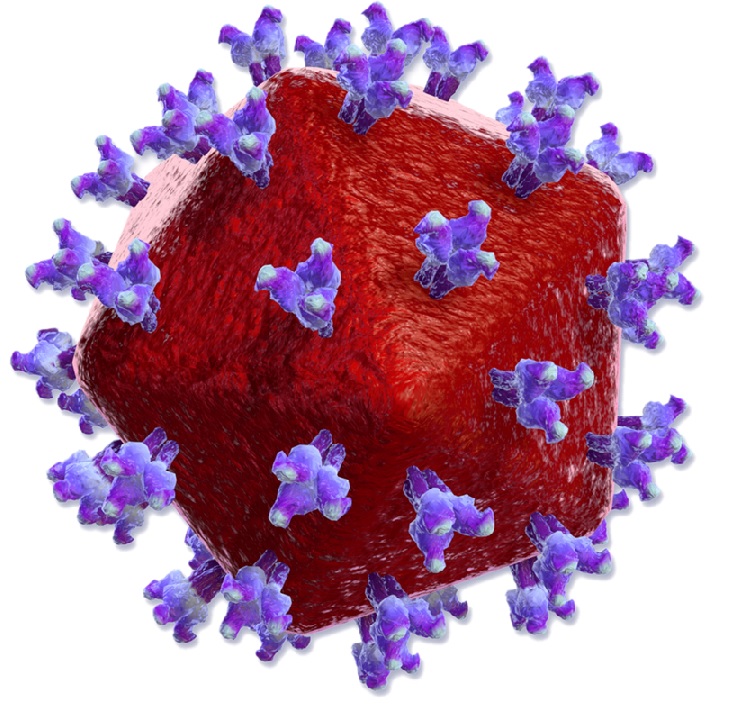
Illustration of HIV virus
By neucrad health February 24, 2019
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are emerging in our society due to polygamy. It is a medical condition which usually spread from infected individuals to a healthy one through unprotected sexual encounters. It is also known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Polygamous people are more susceptible to STD as they opt for more than one sexual partners. However, in some cases, if pregnant mothers have STI, then it may transfer to the unborn child. The causal organisms for these infections are bacteria (gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and syphilis), virus (human papillomavirus, HIV, and genital herpes), and Parasites (trichomoniasis).
How do STDs Transmit from Infected Individuals to Healthy Ones?
These causal organisms for STDs mostly pass through semen, blood, vaginal or other body fluids. STD is a pervasive condition as many individuals having these infections outwardly look healthy and are unaware of the fact of contaminating these diseases. However, the good news is, most of the cases, STD is treatable and can be prevented by following few guidelines. Continue reading to know more about the different types of STDs prevalent among polygamous individuals. Today we are discussing few significant STDs transmitted through polygamy for spreading awareness in our society.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a widespread STD infecting both men and women. Bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common causal organism for Chlamydia infection. It can be very dangerous for women as there are reports of permanent damage to the reproductive system due to this infection. There are reports of ectopic pregnancy and difficulty in conceiving in women affected by chlamydia. Other common complications include infections in urethra, testicles, or prostate gland; and pelvic inflammatory diseases. If pregnant mothers have chlamydia, the newborn may show symptoms of pneumonia, eye infections, or blindness. Common signs of this infection include discomfort during sexual intercourse, pain during urination, yellow or green discharge from the vagina or penis, and pain in the lower abdomen. Antibiotics and the use of latex condoms may be beneficial for this infection. [1]
Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is another common STD transmitted through unprotected oral, vaginal and anal sex with many partners. The causative agent for this infection is a bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Symptoms usually appear after 14 days of inoculating this infection. Men show white, beige, yellow, or greenish pus-like discharge from the penis, urgency of urination and swelling and tenderness in the testicle. Women may experience watery, creamy, or slightly green discharge from the vagina, burning sensation during urination, heavy menstruation cycle, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Doctors diagnose gonorrhoea through blood test and culture test. Common treatment measures include the use of antibiotics like Azithromycin, and the infection can be prevented by proper usage of condoms, having a single sexual partner, or total abstinence of sex with an infected partner. If left untreated it may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, infections in urethra, testicles, or prostate gland, and even infertility. [2]
HIV/AIDS
AIDS is an STD occurring in people infected with HIV. This virus damages the immune system of individuals by killing the CD4 cells in the advanced stages. Though AIDS is an STD, it can also transmit through blood and breast milk. HIV cannot spread through casual body contact, through air, or water, and by sharing food. AIDs is a severe medical condition as there is no cure for this disease. It can be kept under control by the use of antiretroviral therapy medications like nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), protease inhibitors, and integrase strand transfer inhibitors.
Common symptoms of AIDS include recurrent fever, night sweats, chronic swelling in lymph glands especially in the armpit, neck, or groin; and sores or lesions on tongue, genitals, or anus. Physicians prescribe antibody/antigen test and Nucleic acid test (NAT) for the diagnosis of this disease. Till 2016, about 36.7 million people all across the globe were living with active HIV infection. Out of them, a whopping 2.1 million individuals were children below 15 years. Studies reveal that in 2017 approximately 20.9 million patients underwent antiretroviral therapy and leading a normal life with HIV. [4]
Studies reveal though STDs are severe medical conditions, they can be kept at bay substantially by indulging in safe-sex and monogamy.
Image credit: BallenaBlanca, CC