Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)- A Common Hormonal Disorder in Many Women
By Neucrad Health News Desk November 30, 2019
These days many women in their childbearing age get affected by a medical condition called polycystic ovary syndrome or PCOS. Studies suggest that approximately 8-20 per cent of women all across the world suffer from this medical issue. What is more threatening is the fact that numerous women are not even aware that they have PCOS. Most patients with PCOS find it challenging to conceive or going ahead with the pregnancy. However, recent medical advancement, along with weight reduction therapy, has made it possible to keep PCOS and its long-term complications under check if the medical issue gets diagnosed at an early stage. Continue reading to know more about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of PCOS.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
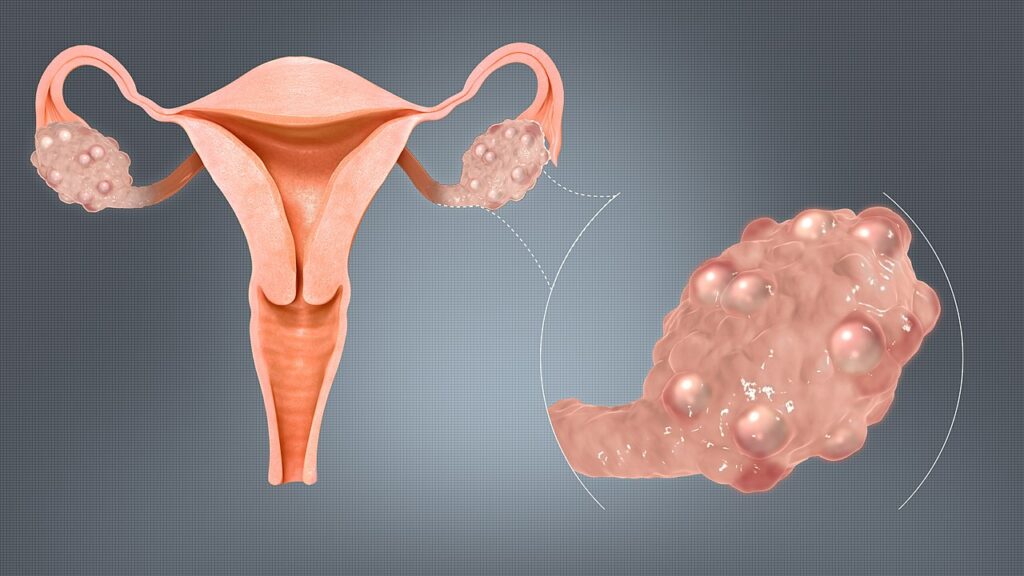
PCOS is a hormonal disorder mostly affecting women in the age group 15 to 44 years. The condition is also known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome. Here, women secrete higher-than-normal level of male hormones (androgens) and develop small fluid-filled vesicles in their ovaries. The cysts contain an immature egg which never gets entirely matured to trigger ovulation. In such a condition, the level of oestrogen, progesterone, FSH, and LH also gets affected.
Usually, these cysts in itself are not harmful to the body, but they can lead to complications if not treated in time. PCOS affects the menstrual cycle, and many women skip their periods altogether. It makes them difficult to get pregnant, as PCOS interferes with the ovulation process. Even after conceiving, it can cause complications like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and pre-term delivery. In many cases, it leads to the growth of facial and body hairs, obesity, acne, and baldness in women. There is also an increased risk of heart ailments, heart ailments, insulin resistance, and diabetes in women having PCS.
What are the causes of PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is still not known to scientists; however, there are some factors which may increase the probability of this condition.
Insulin Resistance
70 per cent of women having PCOS also has insulin resistance where their cells become incapable of utilising insulin. It increases the secretion of androgen, which may lead to the hormonal disbalance.
Low-grade Inflammation
Low-grade Inflammation in the body may also cause PCOS. It increases the chances of heart ailments and blood vessel disorders.
Heredity
If mothers or grandmothers have symptoms of PCOS, then there is a higher probability of daughters demonstrating this symptom in their later age.
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
Detailed below are the common symptoms of PCOS
- irregular menstrual cycle
- higher level of androgen
- high blood pressure
- sleep apnea
- heavy bleeding during menstruation, as the uterine lining gets build up over a long time.
- infertility
- acne
- dandruff
- excess growth of facial and body hair called hirsutism
- obesity
- baldness and thinning of hair
- skin tags on neck, breast and groin area
- depression and anxiety
What are the possible treatments for PCOS?
Doctors usually treat PCOs by recommending lifestyle changes for a reduction in weight. Studies suggest even a 5 per cent drop in body weight can considerably improve the condition. If lifestyle changes do not provide adequate results, then Gynaecologists prescribe a combination of birth control pills containing oestrogen and progestin to reduce the level of androgen. In many cases, metformin and clomiphene have also been effective in controlling the symptoms of PCOS. To reduce excessive hair growth, patients can consider hair removal creams, laser hair removal or electrolysis. If all these treatments fail to provide satisfactory results, then doctors go ahead with surgery to treat the condition.
This was a brief discussion on PCOS. If you or your close relatives are suffering from this condition, do not panic. Seek medical help to control and treat the medical issue.