Doctors often ask to test Thyroid
Thyroid-One of the Crucial Glands in Human Body
Neucrad Health News desk September 17, 2019
Are you feeling fatigued or experiencing difficulty in concentrating on a subject lately? Do you experience increased heart rate and nervousness without any apparent reason in the last few months? If these are related to you, then there are chances that you are suffering from thyroid-related disorders. The small, butterfly-shaped gland present below Adam’s apple plays a crucial role in the wellbeing of human beings. It consists of two lobes and remains connected by a bridge called isthmus. The gland secretes three hormones- Triiodothyronine (T3), Tetraiodothyronine (T4), and Calcitonin. Iodine is an essential element, which acts as the building block of the thyroid gland. Since our body cannot produce this trace element, we need to absorb it through our food for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland. Have a look at the medical conditions due to the over and under secretion of the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism
In the case of hyperthyroidism, the gland becomes over sensitive and starts secreting too much of T3 and T4 hormones. Approximately 1 per cent of women suffer from this condition word wide. Graves’ disease and multinodular goitre often lead to this medical issue.
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Some of the common symptoms due to hyperthyroidism include:
- nervousness
- increased appetite
- restlessness
- increased heart rate
- poor concentration
- irregular heartbeat
- difficulty in sleeping
- itching
- irritability
- brittle hair and nails
- weight loss
- bulging eyes
How do doctors diagnose Hyperthyroidism?
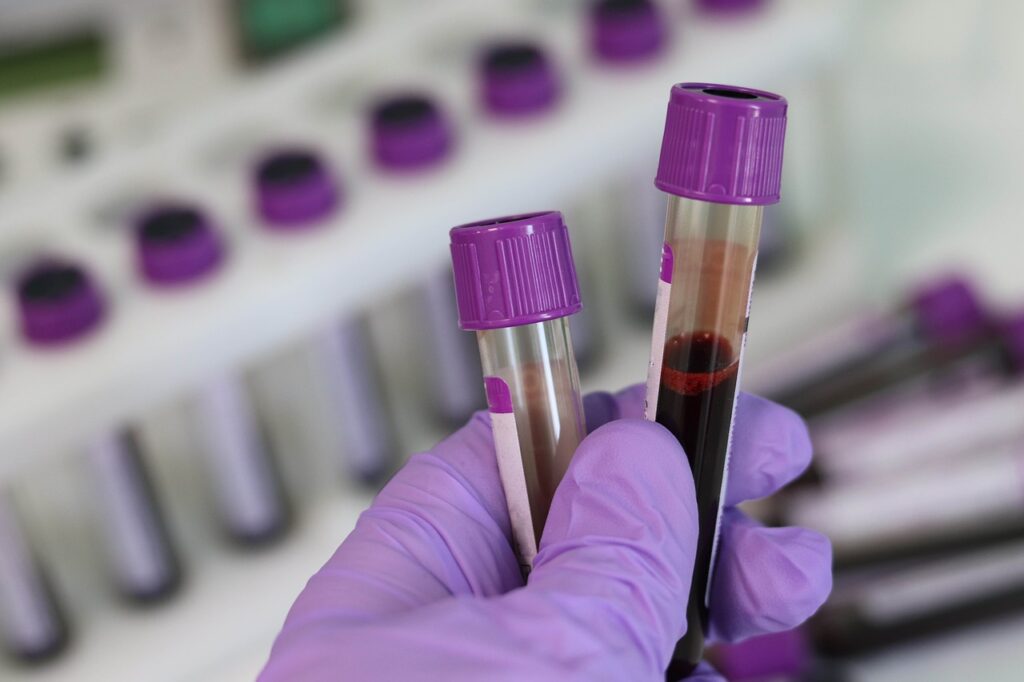
If you experience conditions like weight loss, rapid pulse rate, protruding eyes, high blood pressure and protruding eyes, doctors may prescribe you to undertake a blood test for the estimation of T3, T4, and TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone). If the diagnostic results suggest hyperthyroidism, then the physician may advocate some other confirmatory tests like thyroid scan, ultrasound examination, Computed Tomography (CT Scan), and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan).
What are the treatments for Hyperthyroidism?
The treatment for hyperthyroidism depends on the value of the thyroids hormones. Detailed below are some of the standard form of treatments.
· Control through Medicines
Doctors may prescribe antithyroid medications like Methimazole, Tapazole or Propylthiouracil (PTU) for blocking the activity of the thyroid gland, and hence arresting the secretion of hormones. These medicines have less severe side-effects. Studies suggest that in 20 to 30 per cent cases administration of Methimazole for 12 to 18 months can be effective in prolonged remission of hyperthyroidism.
· Radioactive Iodine
If medicines do not yield satisfactory results, then physicians may also prescribe radioactive iodine either in the oral form or in the injection state. According to American Thyroid Association reports, doctors treat over 70 per cent of U.S. adults with this form of iodine. Since the thyroid cells depend on iodine for their synthesis, they take up the element in any state in the human body. The radioactive iodine makes the hormone-secreting cells ineffective, thereby controlling the production of T3 and T4. The size of the thyroid gland also diminishes, and the level of thyroid hormone reduces from the initial value after this therapy. However, it can lead to some side effects, including dry mouth and eyes, and sore throat.
· Surgery
In some extreme cases, doctors may also surgically remove a section of the thyroid gland. However, it can cause hypothyroidism in future.
Hypothyroidism
This medical condition is the reverse of hyperthyroidism. Here the thyroid gland cannot produce an adequate level of thyroid hormones for the proper functioning of the body. Hashimoto’s disease, thyroid gland surgery, and radiation treatment are some of the common causes of hypothyroidism.
What are the symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
Detailed below are some of the common symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- fatigue
- memory issues
- dry skin
- depression
- becoming sensitive to cold
- slow heart rate
- constipation
- weakness
- weight gain
- coma
How doctors diagnose and treat Hypothyroidism?
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is done through blood tests measuring the value of TSH and thyroid hormone. The primary line of treatment for this medical condition is through the administration of synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine. It helps in maintaining the level of thyroid hormone within the standard range in the blood capillaries.
This was a brief idea about the thyroid gland, its function, and medical issues which can arise due to malfunctioning. Be alert, and regularly go for a health check-up to remain conscious about your health condition.