Woman and Cervical Cancer – an Awareness
Biswarup Ghosh, PhD, Neucrad Health April 5, 2022
Cervical cancer is a deadly disease affecting numerous women across the world. According to the World health organisation (WHO), it is the fourth most frequent malignancies, and in 2018 oncologists detected approximately 570,000 new cases in this field. It constitutes to about 6.6 per cent of all female cancers. In this case, the malignancy starts at the cervix or the opening of the uterus.
Though all women have a risk of developing cervical cancer, ladies above 21 years and those having a family history have a higher risk of developing the disease. In some cases, prolong infection of human papillomavirus (HPV) can also lead to this form of cancer. However, unlike other types of malignancies, scientists have developed a vaccine for cervical cancer. If administered at the right age, it can protect women from this deadly medical condition.
What are the symptoms of cervical cancer?
The early signs and symptoms of cervical cancer include:
- bleeding between periods
- bleeding in post-menopausal women
- discomfort and bleeding after sexual intercourse
- odour emitting vaginal discharge, sometimes it can even contain traces of blood
- pelvic pain
However, it is worth mentioning that many women do not experience any symptoms until the malignancy proceeds to advanced stages. In some cases, the above symptoms can also result from other underlying causes.
How can you undergo screening for cervical cancer?
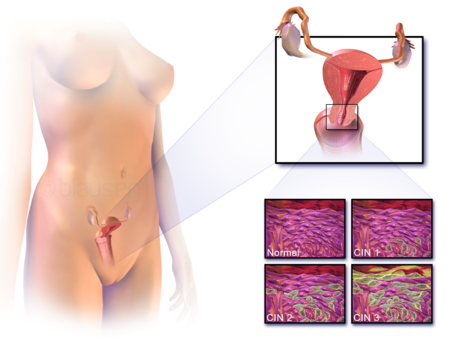
Since cervical cancer is a common type of malignancy; it is essential for women to undergo regular screening for the disease for early detection. Screening also helps in determining precancerous changes and thus help in preventing the disease as well. All adult women above 21, leading an active sexual life should undergo screening procedures at least once in three years for early detection and prevention of cervical cancer. Pap test and HPV DNA test are two crucial screening procedures for this medical condition.
In a pap test, the pathologist scrapes and brushes cells from the patient’s cervix for further cytological examination. If doctors can detect abnormalities in these cells, then they prescribe other confirmatory tests to find out the exact condition of the cervix. In the HPV DNA test, the cervical cells of candidates and examined cytologically for finding out traces of HPV infection.
What are the different stages of cervical cancer?
Oncologists follow a 4-stage system for determining the spread of cervical cancer.
Stage 0: Presence of precancerous cells
Stage 1: Malignant cells are present at deeper tissues of the cervix. Cancer can even spread to other parts of the uterus and adjacent lymph nodes.
Stage 2: Malignancy has advanced beyond the cervix and uterus. However, it did not invade pelvic walls or lower end of the vagina.
Stage 3: Cancer cells restricted to pelvic walls and lower part of the vagina. It may even spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 4: Cancer has invaded to bladder and rectum, and may even spread out to other organs like liver, bones, and lungs.
How can you prevent the occurrence of cervical cancer?
Detailed below are some conventional methods of protecting against cervical cancer.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine
Oncologists have already established a confirmed link between cervical cancer and certain strains of HPV. The administration of the HPV vaccine helps in preventing the occurrence of this malignancy. Doctors are speculating that, if every female receives the HPV vaccine, then it can reduce the incidence of cervical cancer considerably.
Regular Screening for Cervical Cancer
If adult women undergo regular cervical cancer screen procedures, then abnormality in the cervix can get detected at a very early stage. It will help in the immediate treatment of cervical infection and arrest the transformation to cancer.
Safe sex and fewer sexual partners
Women following safe sexual intercourse procedures and limiting the number of sexual partners have a lower risk of developing the disease. Delaying the first sexual intercourse also limits the incidence of cervical cancer.
Follow the preventive procedures and stay protected from this deadly disease.






