Story of India’s success to discover a single pneumonia vaccine against 23 types of bacteria!
Dr. Shuvomoy Banerjee, Neucrad Health Desk, July 24, 2020
United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) recently claimed that more than 600,000 children worldwide suffer from pneumonia, with one child dying of pneumonia every 39 seconds! Of these, the under-two mortality rate is the highest. The five countries that accounted for more than half of all infant deaths were included Nigeria, Pakistan, Congo, Ethiopia and India. According to statistical analysis, India ranks second in the world in terms of infant mortality due to pneumonia. In this alarming situation, the discovery of a special pneumonia vaccine by the Serum Institute of India is like light of the end of tunnel. Specially, it’s a pneumonia-resistant pneumococcal polysaccharide conjugate vaccine (PPSV23) able to prevent 23 types of pneumonia causing bacterial infection has already passed the clinical trial phase-I / II / III successfully. Consequently, the vaccine has received the necessary approval from the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI).
Let’s know more about pneumonia, it’s mode of transmission, and details of this vaccine through our article here.
Pneumonia:
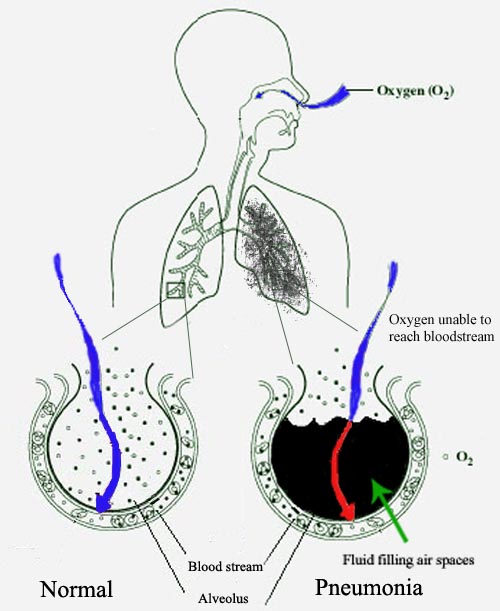
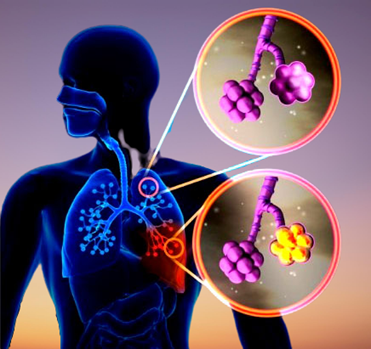
Pneumonia is a disease mainly caused by bacterial, viral and fungal infections. The disease leads to inflammation of the numerous air sacs in our lungs causes accumulation of fluid, pus, etc. to inside the empty space of air sacs. It usually starts with phlegm cough, high fever, headache and shortness of breath and can be fatal if not treated in time. In particular, children under the age of five, older people, and patients with low immunity are at greater risk of pneumonia.

Classification and causal agents of pneumonia:
1. Community Acquired Pneumonia: The most contagious type of pneumonia and following causative agents’ are-
Bacteria– Streptococcus pneumoniae infections cause most of the acute pneumonia in human. This type of pneumonia finally damages single side of the lung or lobe, so such kind of pneumonia is called ‘lobar pneumonia’.
Bacterial-like microorganisms –They cause milder type of pneumonia. Microorganismscalled Mycoplasma pneumoniae are responsible for such pneumonia.
Fungus– People who have been suffering from critical diseases for a long time or who have low immunity, often develop pneumonia due to secondary infection by fungal spores.
Virus– A viral infection can cause mild to severe pneumonia. Children in particular are infected with viral pneumonia. In the case of Covid-19 disease, pneumonia becomes severe and the patient’s condition becomes critical.
2. Hospital Acquired Pneumonia: This pneumonia is caused by a nosocomial infection. The hospitalized patients often develop pneumonia by antibody resistant bacteria. In most of the cases, nebulizers, ventilation, lung surgical instruments can spread the infection from the device.
3. Healthcare Acquired Pneumonia: At various health centers, OPD, Kidney Dialysis Centers, etc., patients get pneumonia through nosocomial infections stated above.
4. Aspiration pneumonia: This type of pneumonia occurs when bacteria contaminated food, drink, saliva, etc. directly reach into the lungs. Such condition can be caused by a nerve disorders, trauma or excessive alcohol and drug consumption.
Pneumonia Vaccine:
The Serum Institute of India conducted their first clinical trial in 2013 among 34 adults. The second trial got successfully completed involving 114 children. Children with age group between six and eight participated in their third clinical trial. Good results were obtained in every clinical trial. The Special Expert Committee (SEC) on behalf of DCGI examined the trial report and allowed their pneumonia vaccine to be released in the market. The vaccine has been used in clinical trials with 2,250 children in the Gambia and has received the necessary approval from the World Health Organization (WHO).
Pneumonia vaccine details:
Scientists purified the capsular polysaccharides from different serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae bacterium. A carrier molecule was also added to enhance the ability of the polysaccharide conjugated vaccine for increasing immunity. Dr. Rajeev Dhere, executive director of the Serum Institute, said the new vaccine would cost much less than other pre-existing pneumonia vaccines used in India. In the next few days, the company will be able to produce 100 million doses per year. For now, 40-50 million doses can be made for India alone.
Scientists believe that with the introduction of this new pneumonia vaccine by the Serum Institute of India, the infant mortality rate will be greatly reduced. The vaccine is also expected to help to prevent pneumonia in people with chronic lung disease or diabetes.

References:
- https://www.seruminstitute.com/news.php
- https://www.who.int/vaccine_safety/initiative/tools/Pneumococcal_Vaccine_rates_information_sheet.pdf?ua=1
- Berical AC, Harris D, Dela Cruz CS, Possick JD. Pneumococcal Vaccination Strategies. An Update and Perspective. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13(6):933-944. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201511-778FR
- Daniels CC, Rogers PD, Shelton CM. A Review of Pneumococcal Vaccines: Current Polysaccharide Vaccine Recommendations and Future Protein Antigens. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2016;21(1):27-35. doi:10.5863/1551-6776-21.1.27
- Verma R, Khanna P. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a newer vaccine available in India. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2012;8(9):1317-1320. doi:10.4161/hv.20654





