Chickenpox- The Most Contagious Infection In Spring
SONY DSC
By neucrad health March 1, 2019
How many of your kids have missed schools at a stretch due to chicken pox? The answer would probably be in affirmation for many of you. Well, chickenpox or varicella is a highly contagious infection occurring primarily in kids during the spring. December to February are the most favorable months for the spread of this disease. Often children in India and other countries of the world miss their school for a long duration as the incubation period varies from 10 to 21 days. Here is a write-up focusing on the causes, symptoms, and treatment of this profoundly dreadful infection of spring months.
What is the Causal Agent for Chickenpox?
The causal organism for chicken pox is Varicella-zoster virus (VZV), and this is the reason the infection is also known as varicella. It can pass on from infected individuals to healthy ones during coughing, sneezing, and saliva; or by direct contact with fluid from the blisters. The person remains contagious from one or two days before the appearance of rashes till all the blisters get crusted over.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Signs of chickenpox are visible for a period of 7 to 21 days. Detailed below are the common symptoms of the disease.
Non-rash Symptoms
∙ Fever ∙ Loss of appetite ∙ Headache ∙ Fatigue
Occurrence of Rashes
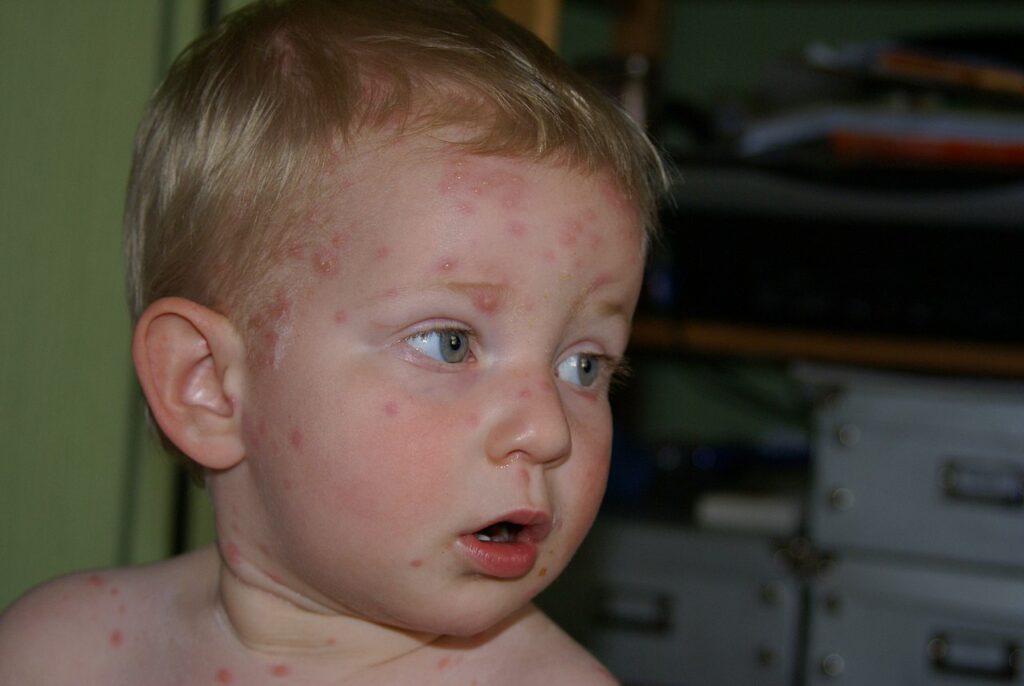
One or two days after the appearance of fever, red or pink fluid-filled rashes develop on the person. Though there are rashes all over the body, all of them are not in the same phase. Here are the three stages of these rashes.
∙ Papules:They are pink or red raised bumps which keep on appearing on the body for several days.
∙ Vesicles:Fluid-filled blisters form after one day of appearance of rashes. It breaks after a few days and the fluid start leaking.
∙ Crusts and Scabs:After the outbreaks start drying up, they form crusts or scabs which take several days to heal. At this stage, they become very itchy.
Who are at a Risk of Developing Chicken Pox?
Risk of acquiring chicken pox increases if you have never suffered chicken pox infection, you are under twelve years of age, have not taken the varicella vaccine, or have a compromised immune system due to certain diseases. Symptoms are often milder with few blisters and no fever in a healthy person. Though the infection usually occurs only once in the lifetime in most individuals, in some rare cases, it may be seen twice.
Diagnosis of Chickenpox
Physicians usually diagnose chickenpox by physical examination of the body and observing the rashes. In some cases, they may prescribe laboratory test.
Treatment of Chickenpox
Since chicken pox is a viral disease, it doe not require any medical treatment. Symptoms become mild as the virus pass on through the system, and the infection runs its course. Doctors usually advocate parent to keep children out of school or day-care for 21 days. They may also prescribe antihistamine medicine to relieve itching. In some rare cases, complications appear, and doctors may recommend antiviral medications to keep the infection under control.
Vaccination for Chickenpox
The best way of preventing chickenpox infection is by the administration of vaccines (Varivax). It offers 94 per cent resistance against the disease. In many countries including India, the varicella vaccine is a part of the routine immunisation programme in kids. Babies receive two doses of this vaccine; the first one is given between ages 12 and 15 months, and the second dose when they reach 4-6 years.
How to Prevent Chickenpox in Unvaccinated children above seven years?
Older children receive two catch-up doses of the varicella vaccine with a gap of 28 days. It helps in preventing the diseases in the majority of the cases. It is also true for adults who have never suffered the disease but wish to avoid the infection. However, doctors do not recommend the vaccines in pregnant women, individuals having a weak immune system due to HIV infection, those undergoing immune-suppressing medications, and people allergic to gelatin or neomycin antibiotic.
So, this was all about chicken pox infection. Get vaccinated and stay away from the general crowd if you are manifesting the symptoms.
Image: An illustration of a child with chickenpox, Phyllis Buchanan,
CC-BY-SA-2.0





